Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return Radiology / Partial anomalous pulmonary venous return | Radiology Case ...
Emergent surgical intervention may be necessary in these cases. Radiologic demonstration of anomalous pulmonary venous connection and its clinical significance. Cases of partial anomalous pulmonary venous return. If there is no obstruction to pulmonary venous return, cyanosis is mild and patients may be minimally symptomatic. Its detection is critical due to the strong association with congenital heart disease as well as other cardiac and respiratory anomalies, which have significant implications for. Total anomalous pulmonary venous drainage; Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection (tapvc) or return (tapvr) is a rare congenital cyanotic heart defect where the four pulmonary veins do not drain into the left atrium but via unique pathways into the right atrium or systemic veins. Prenatal damage to pulmonary vascular bed and extrapulmonary veins.
Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection (tapvc) or return (tapvr) is a rare congenital cyanotic heart defect where the four pulmonary veins do not drain into the left atrium but via unique pathways into the right atrium or systemic veins. In a child born with total anomalous — which means abnormal — pulmonary venous return (tapvr), the pulmonary veins connect to other veins and ultimately drain their blood into the right atrium. Sung wk, au v, rose a. Anomalous pulmonary venous return refers to conditions where some or all of the pulmonary veins have their blood return to the right atrium, either directly or through the svc or an abnormal, connecting venous structure. Cases of partial anomalous pulmonary venous return. Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection(tapvc). Total and partial anomalous pulmonary venous conne. Pulmonary hypertension in a patient with partially anomalous pulmonary venous return.
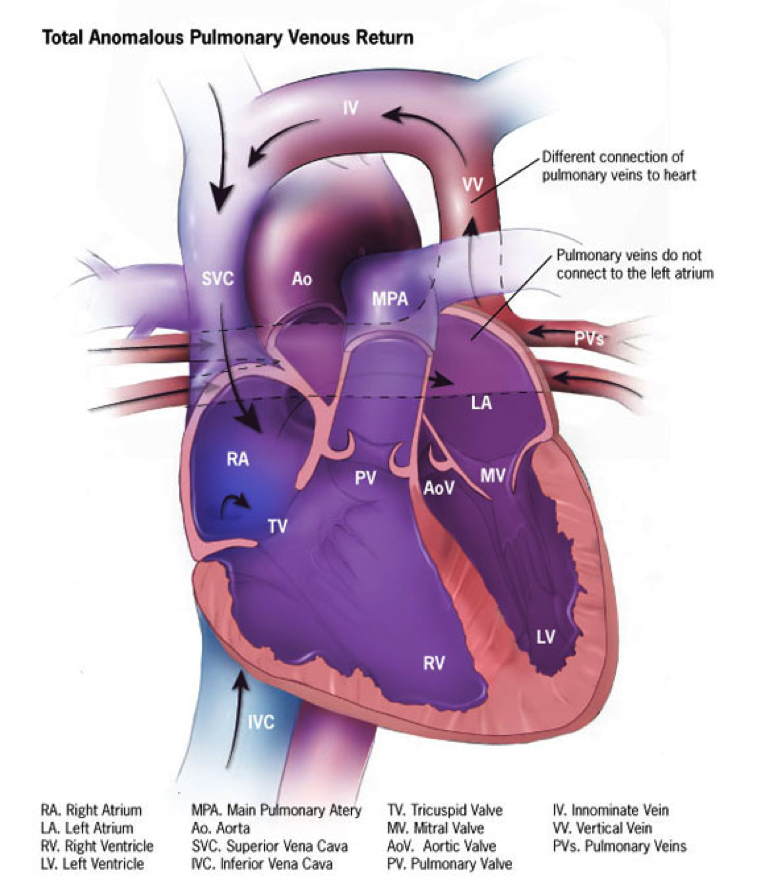
Total anomalous pulmonary venous drainage (tapvr).
Therefore in order to complete the circuit there is almost always an associated shunting defect which is most. Cases of partial anomalous pulmonary venous return. Learn and reinforce your understanding of total anomalous pulmonary venous return. It comprises <1% of all congenital heart defects. Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection (tapvc) is a condition in which all the pulmonary venous return drains either directly into the right tapvc is also referred to as total anomalous pulmonary venous return. Sung wk, au v, rose a. If there is no obstruction to pulmonary venous return, cyanosis is mild and patients may be minimally symptomatic. Causes left to right shunt. This contrasts with partial anomalous pulmonary venous return (papvr) where only part of the pulmonary venous anatomy is abnormal. The role of prenatal diagnosis and pulmonary venous obstruction.
All have shunt through lungs to r side of heart. Anomalous pulmonary venous connection (or anomalous pulmonary venous drainage or anomalous pulmonary venous return) is a congenital defect of the pulmonary veins. Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection (tapvc) is a condition in which all the pulmonary venous return drains either directly into the right tapvc is also referred to as total anomalous pulmonary venous return. All must also have r to l shunt for survival. Total anomalous pulmonary venous return (tapvr) is a condition in which the blood vessels from the lungs take an in tapvr, there is a problem in the usual connection between the blood vessels (pulmonary veins) coming from the lungs to the left atrium. All these partially anomalous pulmonary venous returns are left to right shunts, but when small, they are clinically insignificant. Total anomalous pulmonary venous return:
It then returns through the pulmonary (lung) veins to.
If there is no obstruction to pulmonary venous return, cyanosis is mild and patients may be minimally symptomatic. Anomalous pulmonary venous connection is a rare cyanotic congenital heart defect in which all four pulmonary veins are malpositioned and make anomalous connections to the systemic venous. Total anomalous pulmonary venous drainage and coarctation of the aorta. Total anomalous pulmonary venous return: Isolated partial anomalous pulmonary venous connections in adults: Partial anomalous pulmonary venous return (papvr). Although several different classification systems have been proposed for. Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection (tapvr) is a rare lesion with the pulmonary veins commonly connecting to a venous confluence that ultimately drains to the desaturated atrial chamber. All must also have r to l shunt for survival. Experience of 84 cases from 1 medical center. Papvc or partial anomalous pulmonary venus return (papvr) has a prevalence of.
All must also have r to l shunt for survival. Therefore in order to complete the circuit there is almost always an associated shunting defect which is most. This contrasts with partial anomalous pulmonary venous return (papvr) where only part of the pulmonary veins are abnormal. In this heart defect, some but not all of the lung blood vessels (pulmonary veins) are attached to the wrong place an echocardiogram is generally used to diagnose total anomalous pulmonary venous return. A pediatric radiology textbook and pediatric radiology digital library.
Total and partial anomalous pulmonary venous conne.
Partial anomalous pulmonary venous return in patients with pulmonary hypertension. The cause of the problem is not known. It comprises <1% of all congenital heart defects. Emergent surgical intervention may be necessary in these cases. Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection(tapvc). Its detection is critical due to the strong association with congenital heart disease as well as other cardiac and respiratory anomalies, which have significant implications for. Cases of partial anomalous pulmonary venous return. Sung wk, au v, rose a. Total anomalous pulmonary venous drainage (tapvr). This contrasts with partial anomalous pulmonary venous return (papvr) where only part of the pulmonary veins are abnormal. (papvc), pulmonary vein stenosis and hypo.
All these partially anomalous pulmonary venous returns are left to right shunts, but when small, they are clinically insignificant anomalous pulmonary venous return. Patients with obstructed total anomalous pulmonary venous return are usually critically ill with severe cyanosis and often have very unstable blood pressure.

Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection.

Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection (tapvr) is a rare lesion with the pulmonary veins commonly connecting to a venous confluence that ultimately drains to the desaturated atrial chamber.

Echocardiographic diagnosis of anomalous pulmonary venous connections;

Total anomalous pulmonary venous return:

Posted by rathachai kaewlai, m.d.

Total anomalous pulmonary venous drainage and coarctation of the aorta.

A pediatric radiology textbook and pediatric radiology digital library.

Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection;
J med imaging radiat oncol.

It then returns through the pulmonary (lung) veins to.

In a child born with total anomalous — which means abnormal — pulmonary venous return (tapvr), the pulmonary veins connect to other veins and ultimately drain their blood into the right atrium.

Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection.

(papvc), pulmonary vein stenosis and hypo.

It comprises <1% of all congenital heart defects.

Partial anomalous pulmonary venous return (papvr).

J med imaging radiat oncol.

Partial anomalous pulmonary venous return (papvr).

Partial anomalous pulmonary venous return (papvr).

Emergent surgical intervention may be necessary in these cases.

The cause of the problem is not known.

J med imaging radiat oncol.

Total anomalous pulmonary venous return.

Prenatal damage to pulmonary vascular bed and extrapulmonary veins.

Total anomalous pulmonary venous drainage (tapvr).

Must have atrial septal defect or patent foramen.

Anomalous pulmonary venous connection is a rare cyanotic congenital heart defect in which all four pulmonary veins are malpositioned and make anomalous connections to the systemic venous.
Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection(tapvc).

It then returns through the pulmonary (lung) veins to.
Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection(tapvc).

This condition may also be called partial anomalous pulmonary venous connection (papvc).

Total anomalous pulmonary venous return.

All must also have r to l shunt for survival.

Anomalous pulmonary venous connection is a rare cyanotic congenital heart defect in which all four pulmonary veins are malpositioned and make anomalous connections to the systemic venous.

Total neonatal outcomes in total anomalous pulmonary venous return:

Emergent surgical intervention may be necessary in these cases.

Posted by rathachai kaewlai, m.d.
Posting Komentar untuk "Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return Radiology / Partial anomalous pulmonary venous return | Radiology Case ..."